The papers in this issue of JFDE discuss the potential of adaptive building envelopes, component development as well as implementation strategies
Editorial
-
103
The papers in this issue of JFDE discuss the potential of adaptive building envelopes, component development as well as implementation strategies. The applied practice paper demonstrates decision strategies behind the adaptive sun shading system of the Al-Bahr Towers. Additivity in building envelopes is not only a strategy to fulfil the growing demands for energy efficient buildings and comfort but has great architectural implications as well. In general it asks for more complex components as well as control strategies. But complexity also means costs and risks, and we need to discuss...
Articles
-
105-127
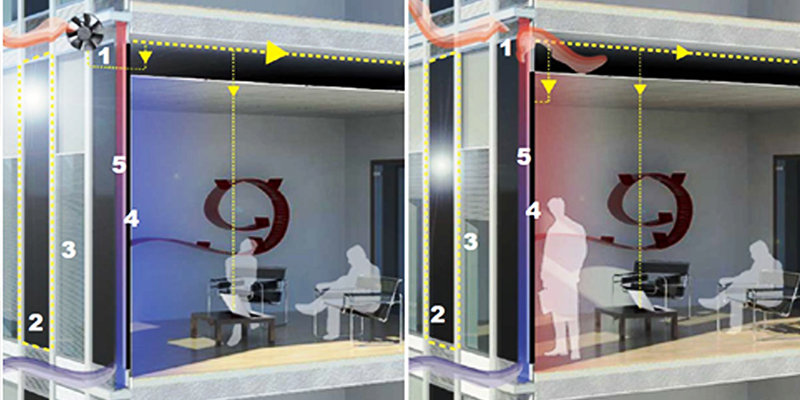
The growing demand for both building energy efficiency and indoor environmental comfort is leading to a substantial evolution of the traditional concept of the building envelope. The future building skin is required to be responsive and dynamic, actively regulating the flows of heat, light, air and water from outdoor to indoor and vice versa, in order to effectively respond to ever-changing climatic conditions, occupant comfort and energy efficiency requirements. In the framework of a decade-long research activity on Advanced Integrated Facade, AIF, a new Multifunctional Facade Module...
-
129-141
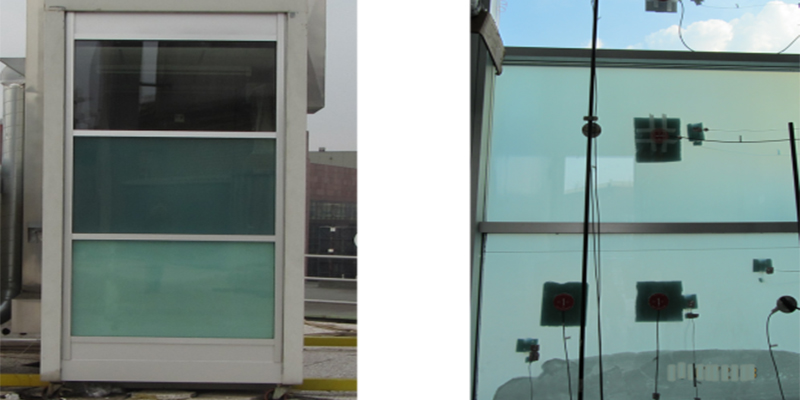
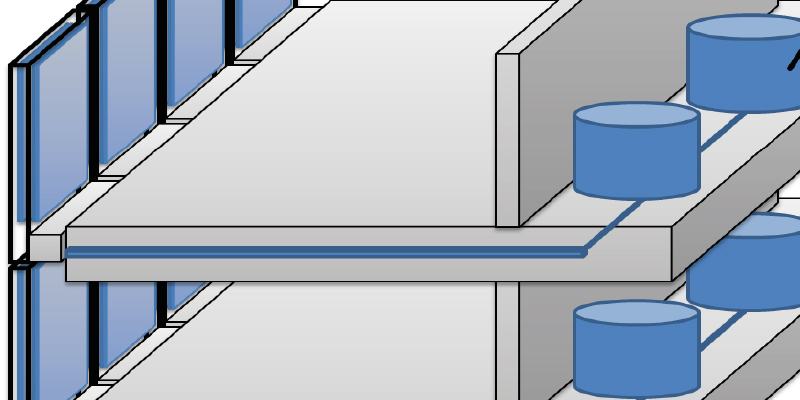
The energy demand for operating modern office spaces is often driven by either the annual heating demand, cooling demand or the demand for electrical lighting. The irradiation of the sun directly and indirectly affects the demand of all three. Consequently, the glazing of higher office buildings is often treated with coating that allows a fixed transmittance. Due to changing exterior conditions and interior needs, a fix-transmittance value is a compromise and most often doesn’t provide optimal thermal and visual conditions. The team in the research project named Fluidglass develops a new...
-
143-163
The key role of the building envelope in attaining building energy efficiency and satisfactory indoor comfort has long been established. Nevertheless, until recent times, all efforts and attention have mainly been focused on increasing and optimizing the thermal insulation of the envelope components. This strategy was a winning approach for a long time, but its limitations became obvious when users and designers started to consider the overall energy demand of a building and started to aim for Zero Energy Building (ZEB) or nearly ZEB goals. New and more revolutionary concepts and...
-
165-183
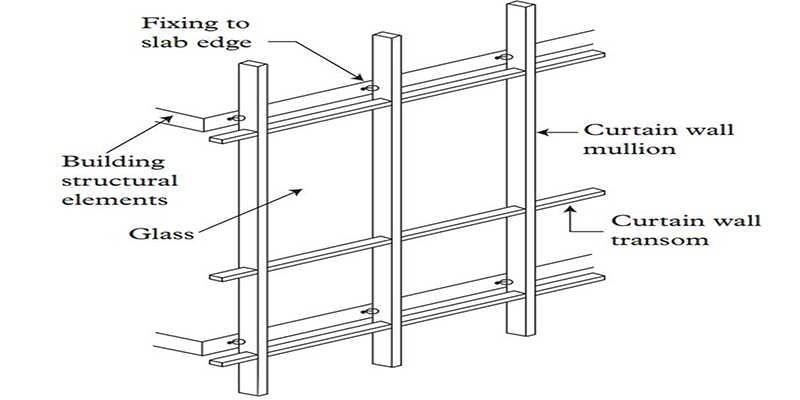
Building facade has a significant impact on the environmental and economic performance of buildings and projects. The specification of their elements at the early design phase depends on numerous technical, environmental and economic factors and involves several stakeholders. The procurement and delivery of the facade work package from the early design phase, through detailed design and manufacture, to installation is a process with several inherent risk factors due to the involved cost, technical and engineering complexities and its position on the critical path in all projects. This...
Applied practice
-
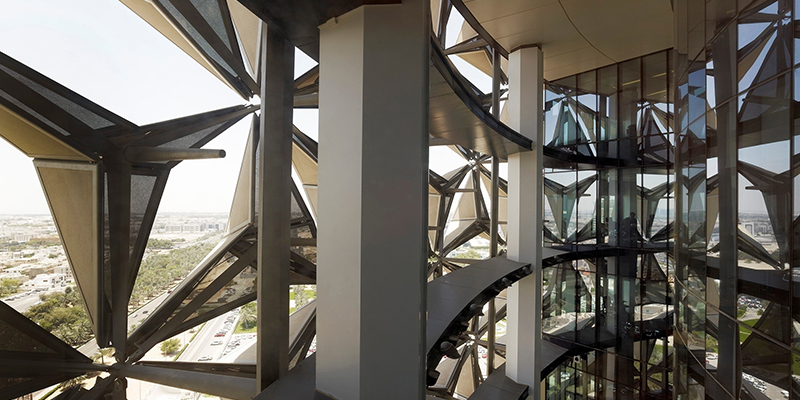
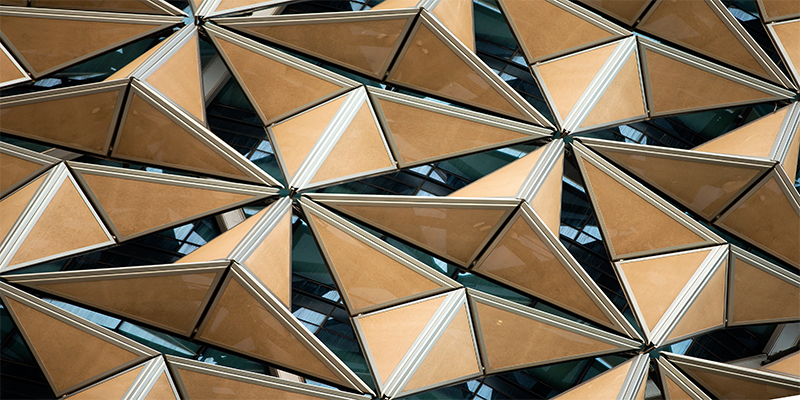
High performance adaptive solutions are capable of responding to the dynamic nature of users and context. These innovative and dynamic systems are steadily gaining ground over ubiquitous ‘best fit’ static models. These architectural elements often exist beyond the scope of mainstream building standards and traditional methods for data representation or communication. This presents major challenges to a highly standardized and compartmentalized industry in which ‘innovation’ is limited to a few signature practices that design iconic yet expensive structures, which often prioritize...