Editorial
-
Buildings are the largest consumer of energy demand and the largest emitter of greenhouse gases. More than the 50% of the residential buildings in Europe were built before 1970; the renovation and upgrading of the existing buildings is a priority in the EU energy policies and in all the EU member states. Increasing focus on energy conservation necessitates the adoption of innovative materials. Government regulations and support for zero energy buildings provide an impetus to the adoption of innovative materials (Directive 2010/31/EU)
AMANAC is a collaboration and...
Articles
-
3-18
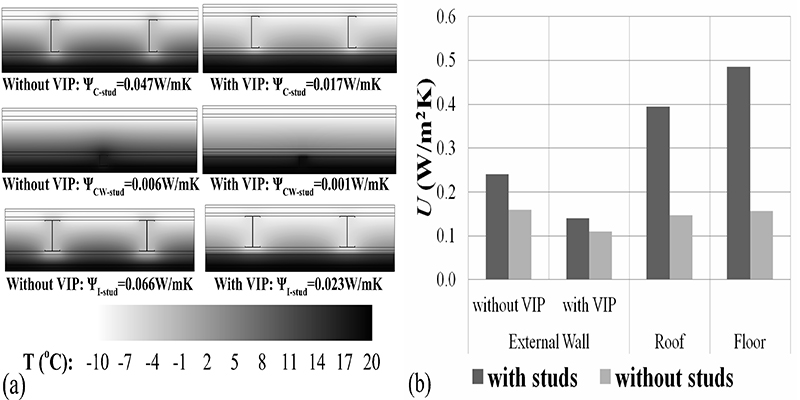
This paper addresses the thermal bridges issues of a two storey lightweight steel framed envelope in which the VIPs are placed in an inner “protected” layer of the external walls. This configuration provides “protection” for the VIPs, allows flexibility in installation of façade elements and at the same time permits interventions and modifications (e.g. drilling, installation of appliances) on the internal side of the wall. The envelope is extensively analyzed in terms of all the different types of thermal bridges utilizing commercial computational tools and standardized methodologies...
-
19-34
In France, and in Europe in general, the building sector is the largest consumer of energy and accounts for about 43% of the total energy consumption and around 25% of CO2 emissions [1]. The building sector offers significant potential for improved energy efficiency through the use of high-performance insulation and energy-efficient systems
In this study, the thermal behavior of buildings with an advanced thermal insulation system, particularly, with the aerogel-based rendering/mortar exterior insulation system is examined. In addition to new buildings, the rendering is very...
-
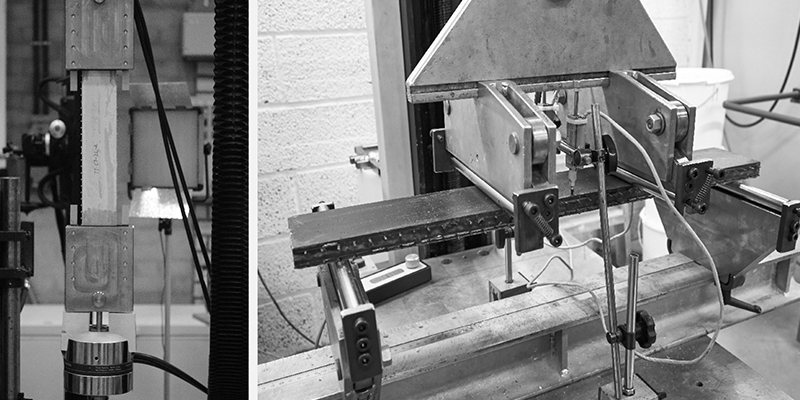
To take structural aspects into consideration in the SESBE research project, focusing on the development of “smart” façade elements a systematic testing and modelling program has been developed for the verification of the structural performance of the façade sandwich elements.
The present paper mainly focuses on the verification of the mechanical performance of the glass fibre reinforced polymer (GFRP) connectors of the novel type of façade element composed of reactive powder concrete (RPC) panels...
-
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) is a fairly novel material with extraordinary strength and durability properties. Due to these properties, it is increasingly being utilized for external facade cladding thus enabling a considerable reduction in the thickness of concrete elements. Commercial RPC formulations on the market are usually expensive and less sustainable due to high cement clinker contents. In this study, improved RPC formulations with higher amounts of supplementary cementitious...
-
Biocomposites are made of natural fibers which are an attractive alternative to conventional synthetic fibers such as glass or carbon fibers not only because their intrinsic properties but also because their contribution to more sustainable materials. However, natural fibres are flammable and the biocomposites need to be protected against fire for safety reasons but also to meet the strictest EU regulations of the transport and construction sectors. Thermosetting composites need high loadings of flame retardant additives to achieve satisfactory results in terms of flammability....