Guest Editors: Julen Astudilllo Larraz and Jose Antonio Chica
ISBN 978-94-6366-051-8
Full Issue
Editorial
-
Dear Scientists, Engineers, and Designers,
With this new edition we continue the collaboration with our funding member Tecnalia and the International Congress on Architectural Envelopes (www.icae2018.eu), which they organise every 3 years in San Sebastian (Basque Country, Spain).
The eleven articles found in this new issue were carefully selected from 50 abstracts that will be presented during the scientific section of the congress. The final selected papers were subjected to the regular...
Articles
-
001-008
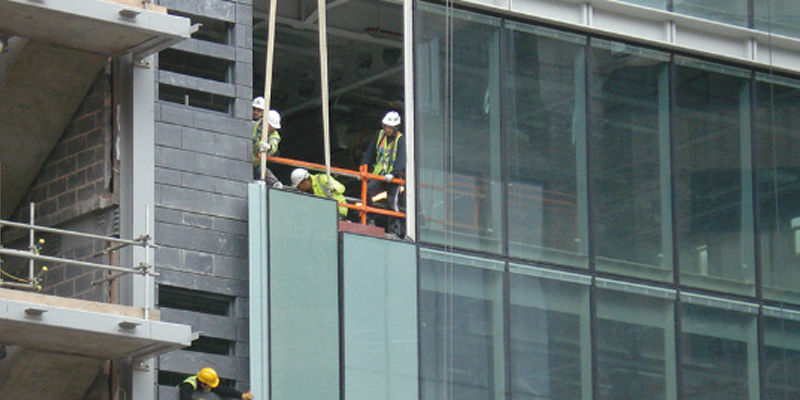
The installation of façade enclosures is a manual, dangerous, and time-consuming construction task. However, thanks to the capability of automated systems, the application of automation in construction is increasing, and therefore, manual work and risky situations can be avoided. Despite this, only a few robotic systems are capable of spanning such a vast work space, i.e. the façade of a building. Among these systems is the cable driven parallel robot (CDPR). Furthermore, the CDPR could carry heavy loads such as unitised curtain...
-
The integration of active solar thermal technologies into building envelopes has recently received a rising attention, promoted within international projects as IEA Task 56 or Cost Action 1403. Although the façade integration of solar thermal collectors is a long debated topic, less attention is paid to the building integration of solar water storages.
The scope of the paper is to highlight the main barriers experienced in the development of a façade-integrated solar water storage. This activity is a part of the SunRise project that aims to develop new unitized curtain wall... -
021-028
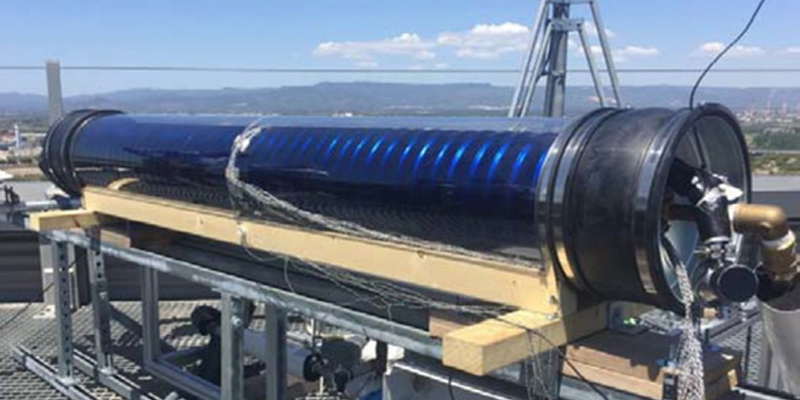
The development of novel systems for the on-site integration of renewable energy in buildings is increasingly demanded for the reduction of the energy consumption resulting from domestic hot water, heating and cooling usages. Within this context, the development of efficient solar collectors for domestic hot water demand production that benefit from their architectural integration in buildings is of high relevance.
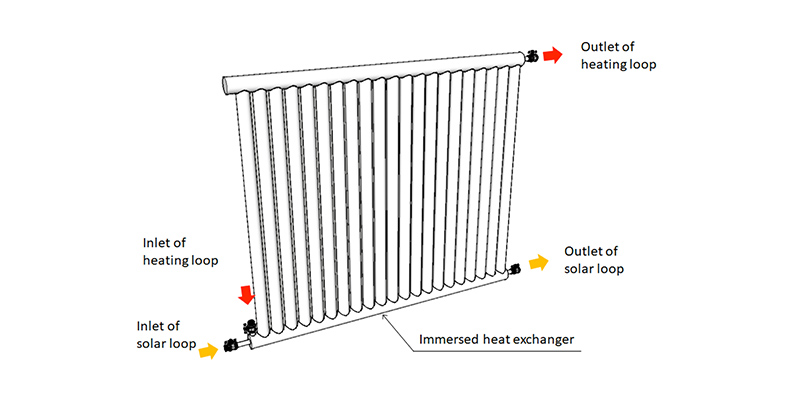
In the present study a novel solar collector device with a tube-in-tube concept that integrates domestic hot water storage and absorber in a single unit, is tested...
-
029-040
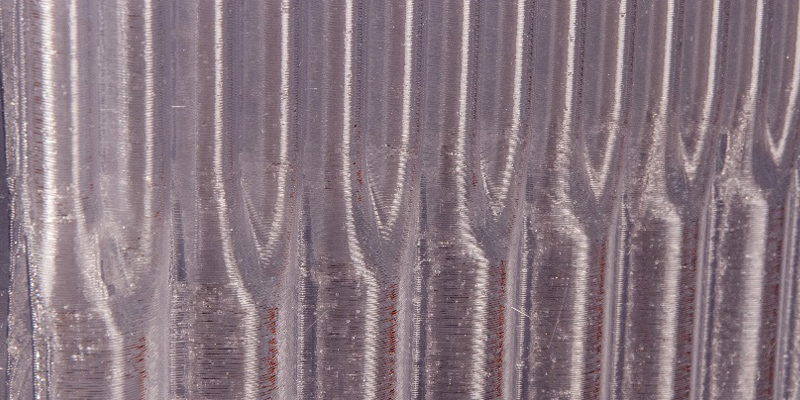
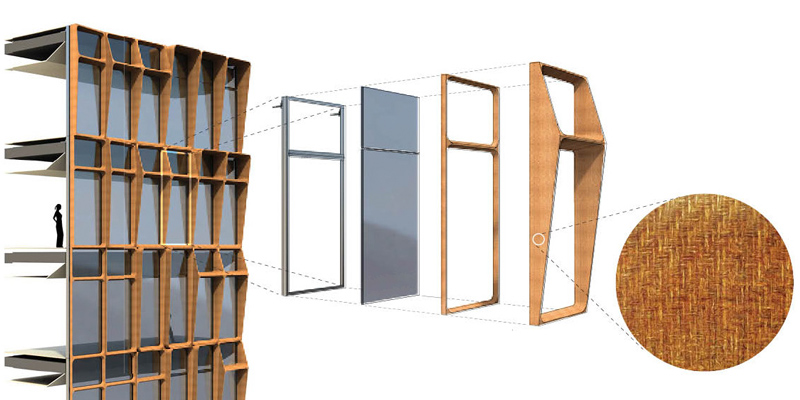
Currently, several research projects investigate Additive Manufacturing (AM) technology as a possible construction method for future buildings. AM methods have some advantages over other production processes, such as great freedom of form, shape complexity, scale, and material use. These characteristics are relevant for façade applications, which demand the integration of several functions. Given the established capacity of AM to generate complex geometries, most existing research focuses on mechanical material properties and mainly in relation to the load-bearing capacity and...
-
041-051
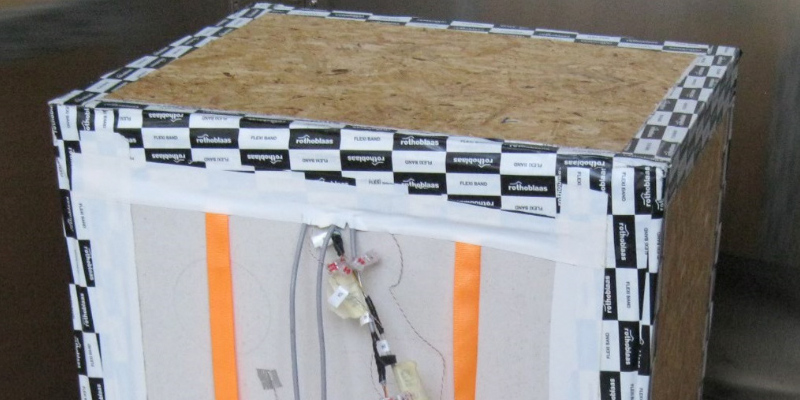
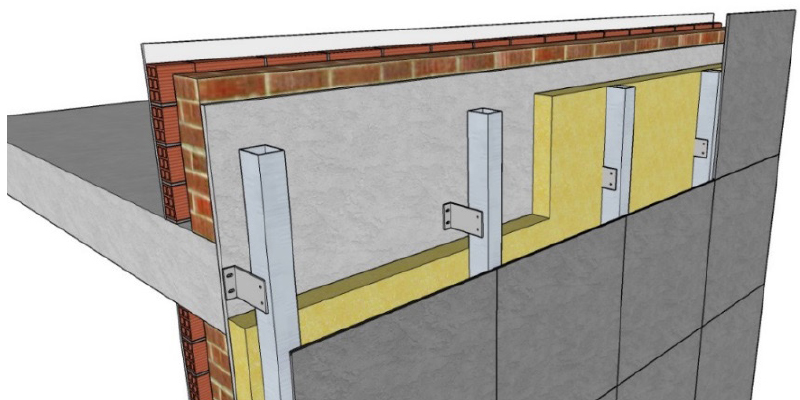
Vapour barriers and retarders are often needed to improve the hygro-thermal performance of the building envelope. Their use is particularly important in prefabricated timber façades, especially when critical boundary conditions occur. In the literature, very little is known about the actual performance of complete envelope packages that integrate these membranes, since most previous studies focused on the analysis of single components. However, considering the growing interest and use of such timber facade elements, an analysis of the performance of integrated membranes is...
-
053-063
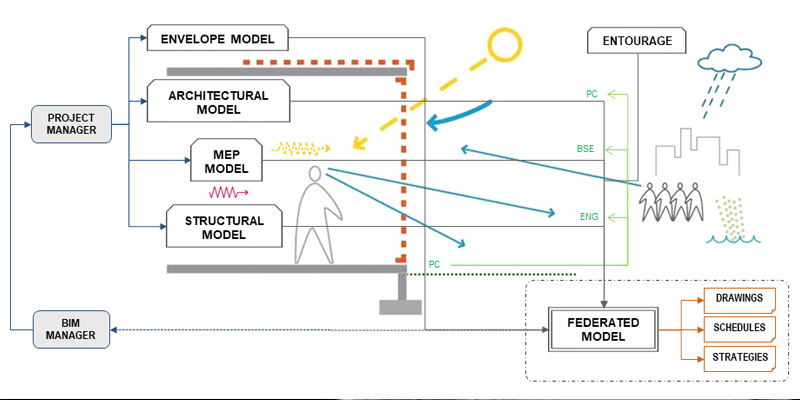
When an architect ideates a complex building envelope, they often rely on a façade consultancy to develop the final detailed solution of their design. The purpose of this paper is to describe a customised BIM methodology to develop complex building envelopes, evaluating the process followed to convert an architectural concept design to a fabrication reality.
Over recent years, building information modelling has developed greatly in terms of architectural, structural and MEP disciplines. It conveniently advances and analyse the variables of a concept design,...
-
Osirys is a European Research Project where a holistic solution for façades and interior partitions ready to be applied in building retrofitting and new construction has been developed. The project uses biocomposites as the base material to define different products: a multilayer façade, a curtain wall, a window, and an interior partition. The biocomposites developed have different functionalities able to meet the strictest requisites of the European Building Codes in relation to fire and structural performance, improve indoor air quality through the elimination of VOCs (volatile organic...
-
085-094
There is a clear trend towards the increased contribution of renewable energy at European level, and EU policies are oriented towards that direction. The building sector is no exception and presents an urgent necessity for increasing the share of renewable energy sources (RES) to reduce the impact on the environment.
The aim of this paper is to examine the potential of solar heating and cooling technologies in reducing energy consumption by incorporating solar thermal and PV collectors within the building’s envelope. Although generally envisaged to be integrated in the roof,...
-
095-106
A methodological approach to the multi-dimensional heat transfer assessment of building envelopes is performed. The proposed method focuses on thermally weak points in envelope-structure junctions and the assessment of envelope retrofit alternatives. Thermal performance in these spots is seldom assessed in energy audit processes, although it is one of the main heat loss paths in many insulated façade solutions. An envelope-slab junction case is presented, where multi-dimensional heat transfer occurs. This paper proposes a methodology that allows for a hybrid experimental and...
-
107-117
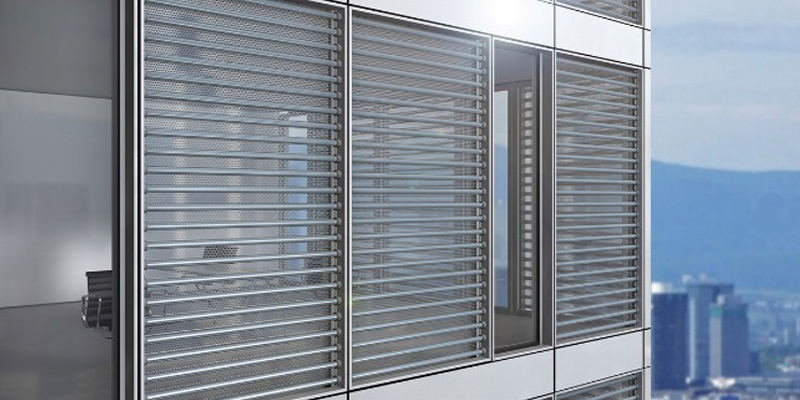
Climate Adaptive Facades are considered promising breakthroughs for the reduction of energy consumption, as energy exchange is enabled when the weather conditions offer benefits instead of threats. So far, conventional building envelops enhance thermal performance through opaque façade components and static insulations. Therefore, natural resources from the building environment remain untapped. Little research has been done in Adaptive Opaque Facades, even if their dynamic behaviour shows a strong potential to exploit environmental resources. For the successful development of these...
-
119-131
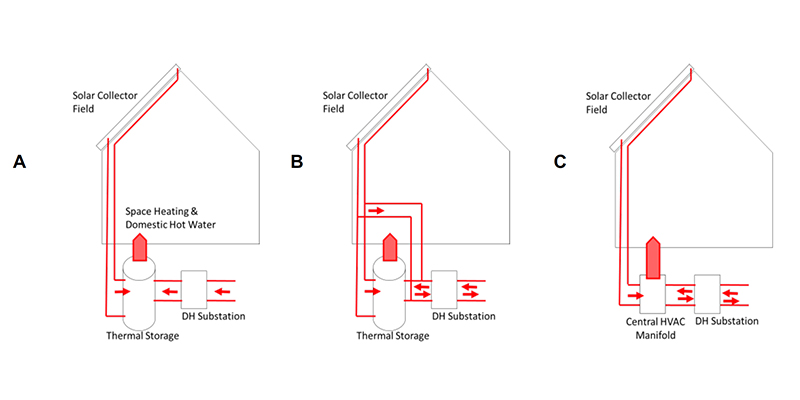
In this paper, the energy performance of a solar thermal (ST) façade system is studied in relation to its connection to a district heating system. This concept allows for the direct use of ST heat in the building, while taking profit from the network for delivery/selling of excess heat and purchase of heat during periods of underproduction. The use of unglazed collectors for low-intrusive architectural interaction in façades is discussed.
Studies are carried out on the heat production of the system and its capacity to cope with local demands. Economic...