Guest Editors: Andreas Luible, Laura Aelenei, Marco Perino, Frank Wellershoff and Uta Pottgiesser
ISBN 978-94-6366-099-0
Full Issue
Editorial
-
This special issue is linked to the conference FAÇADE 2018 – Adaptive!, the fifth conference that is organised by Lucerne University of Applied Science and Arts within the framework of the European Façade Network EFN. FAÇADE 2018 is also the final conference of the COST Action TU1403 “Adaptive facades network” (www.tu1403.eu) and dedicated to multifunctional, adaptive and dynamic building envelopes.
Approximately one third of all end-user energy in Europe today is consumed by space heating / cooling, ventilation and lighting of...
Articles
-
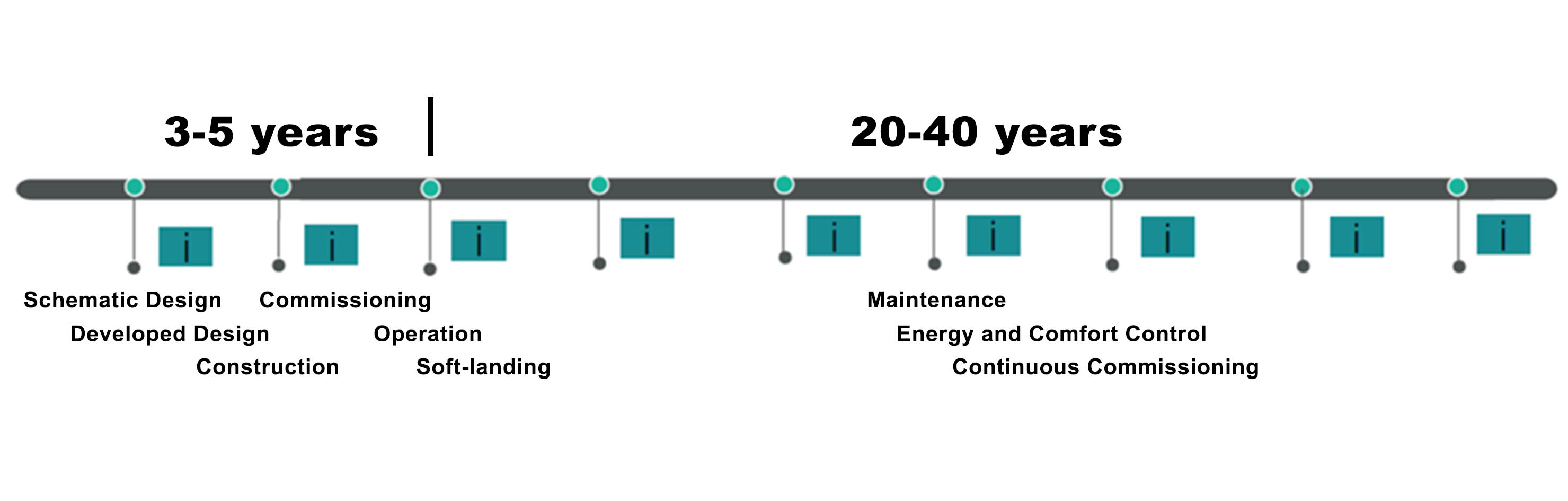
Post-occupancy evaluation is a valuable method of generating information on the performance of adaptive building façades in relation to users. This evaluation technique involves both procedural methods, such as soft-landing, and empirical measuring, such as environmental monitoring or self-reporting techniques including surveys. Several studies have been carried out in recent decades to identify the most appropriate methods for occupant comfort, well-being, productivity, satisfaction, and health assessments in workplaces. Post-occupancy evaluation of adaptive façades can, however, be a...
-
10-18
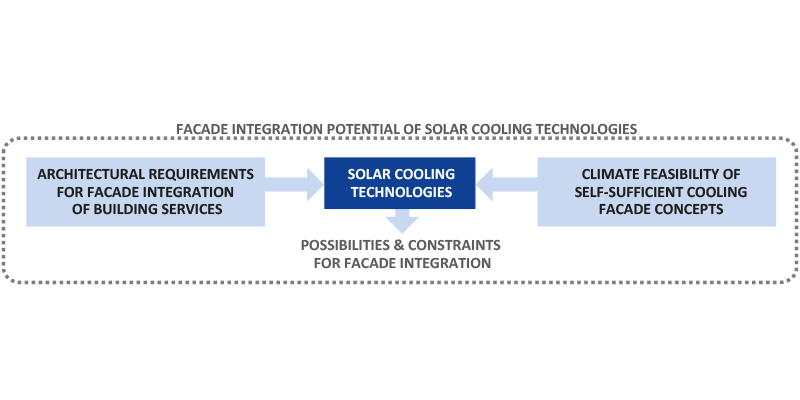
Cooling demands in buildings have drastically increased in the last decades and will follow that trend in the near future, due to increasing standards of life and global climate change among the most relevant factors. Besides energy consumption, the use of refrigerants in common vapor compression cooling technologies is a source of concern for their environmental impact. Hence, there is a need to decrease cooling demands in buildings while looking for alternative clean technologies to take over the remaining loads. Solar cooling systems have gained increased...
-
19-33
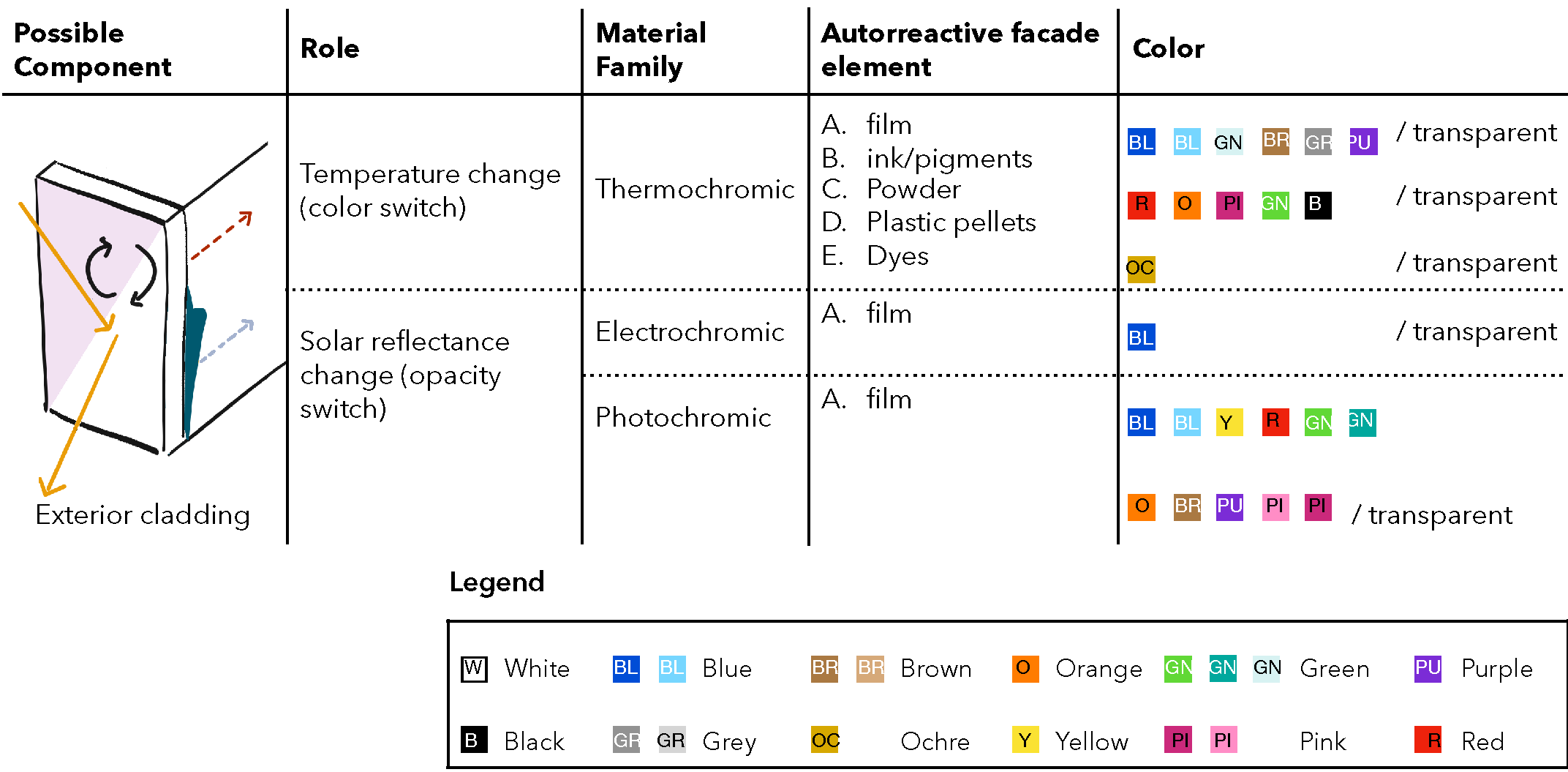
Today’s society needs to face challenging targets relating to environment and energy efficiency, and therefore the development of efficient façade systems is essential. Innovative concepts such as Adaptive Building Façades might play a role in the near future, as their dynamic behaviour could optimise the performance of a building. For their successful development, a balance between sophistication and benefit is necessary and the implementation of Smart and Multifunctional Materials in building envelopes could be the key, as they have the ability to repeatedly and reversibly change some...
-
34-48
Ventilated façades are applied in both new and existing buildings. It has been claimed that these components help to reduce energy use in buildings and improve occupant comfort. However, their performance strongly depends on the airflow passing through the cavity. In order to characterise and to model the behaviour of the ventilation and its effectiveness, the components need to be tested in the laboratory, as well as under real dynamic weather conditions. Despite the steadily growing research in this area, there are few studies with conclusive results about...
-
49-64
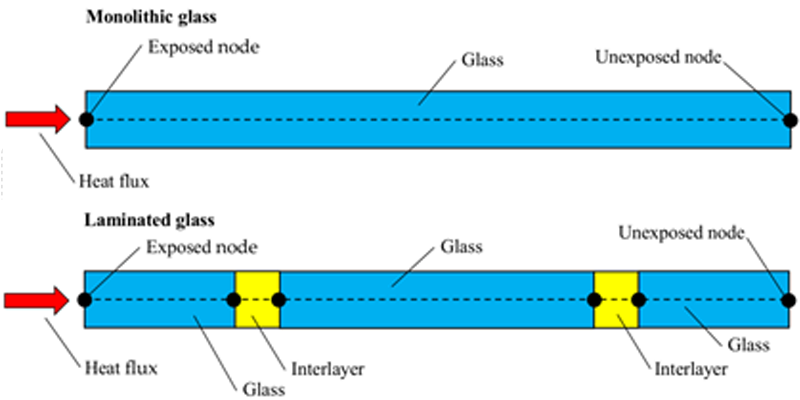
Nowadays, glass is increasingly being used as a load-bearing material for structural components in buildings and façades. Different structural member solutions (such as panels, beams, columns) and loading conditions were the subjects of several research studies in recent years. Most of them, however, were typically limited to experimental testing and numerical simulations on glass elements and assemblies at room temperature. Thermo-mechanical investigations, inclusive of the temperature-dependent behaviour of visco-elastic
interlayers used in laminated glass solutions, as well as the... -
65-76
Adaptive façades can improve the building’s energy efficiency and economics, through their capability to change their behaviour in real time according to indoor-outdoor parameters, by means of materials, components, and systems. Therefore, adaptive façades can make a significant and viable contribution to meeting the EU´s 2020 targets. Several different types of adaptive façade concepts have already been developed, and an increase in emerging, innovative solutions is expected in the near future. According to recent research, the word ‘adaptive’ in the context of building façades is often...
-
Although their potential for high environmental performance is largely accepted, adaptive façades have not yet become widespread in practice. Most of the current examples are developed by engineer-to-order design processes, as project-oriented, custom, and complex solutions. More simple and reliable solutions are needed to support the reuse of technical solutions between projects and increase the feasibility of adaptive façades. Therefore, this research aims to develop a procedure to design adaptive façades whose parts are based on engineered standard products with the least number of...
-
101-115
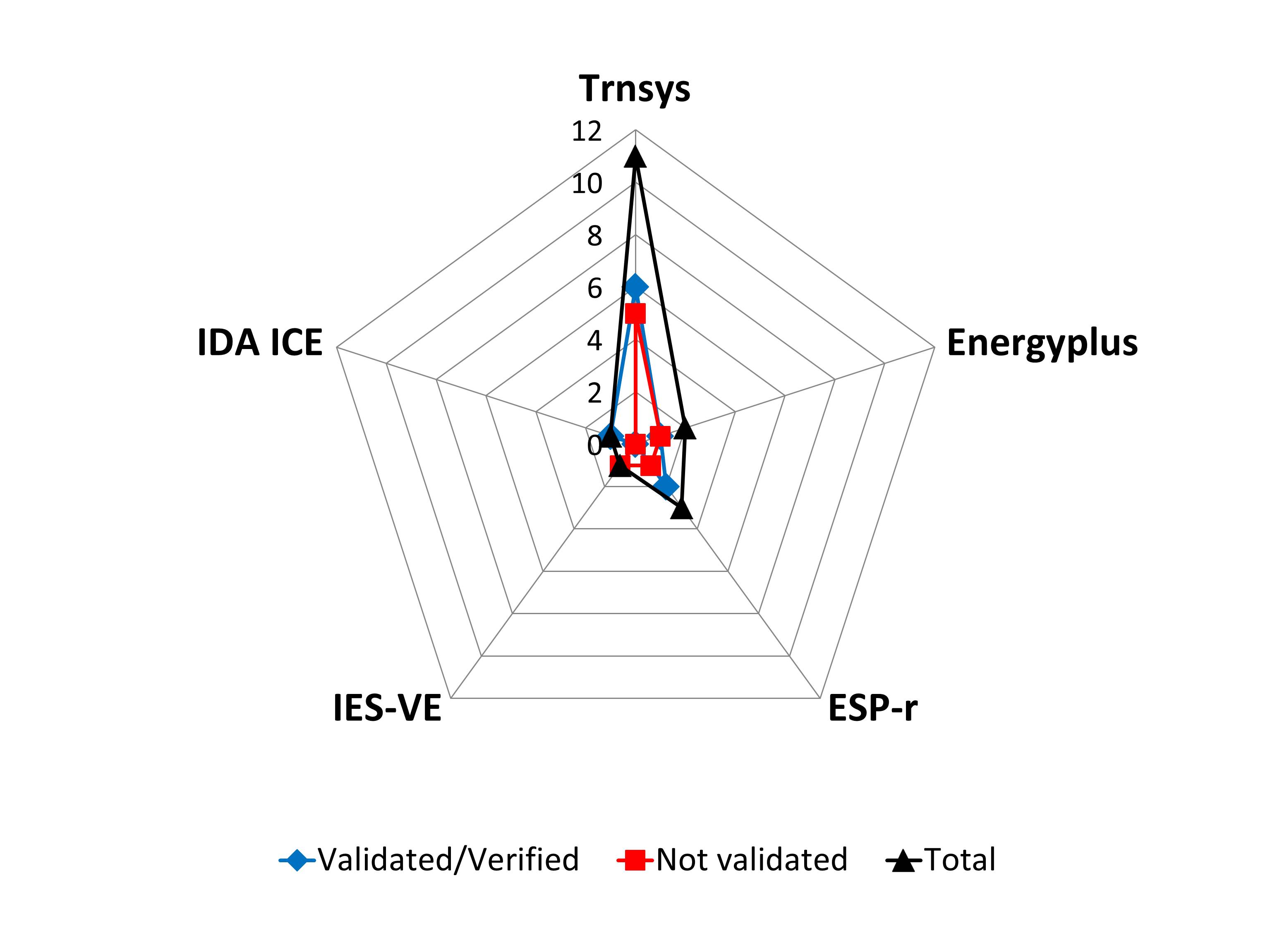
This article presents an overview of possibilities and points of attention for modelling the performance of dynamic CFS in building performance simulation software. Following a detailed analysis of the unique requirements that are associated with modelling of CFS, a comparative study of the capabilities in different software implementations is presented. In addition, we present on overview of state-of-the-art approaches to obtain the necessary Bi-directional Scattering Distribution Functions (BSDF), involving experimental characterisation, databases, and component-level ray-tracing...
-
116-131
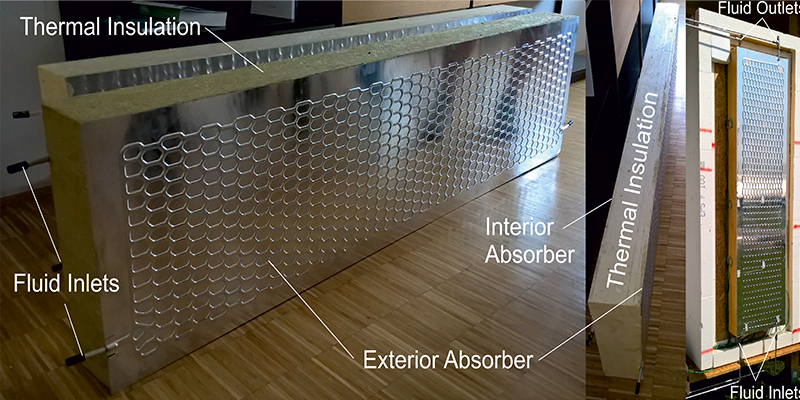
Conventional sandwich panels are one of the cheapest and easiest solutions for forming the thermal building envelope of industrial buildings. They are pre-fabricated façade elements, of which millions of square metres have been produced and mounted every year. There is great potential to reduce the consumption of fossil fuels and CO2 emissions through the solar thermal activation of such a sandwich panel. In the course of the research project ABS-Network SIAT 125, a Solar Thermal Activated Façade (STAF) panel was designed which is to be optimised both thermally and structurally. This...
-
132-148
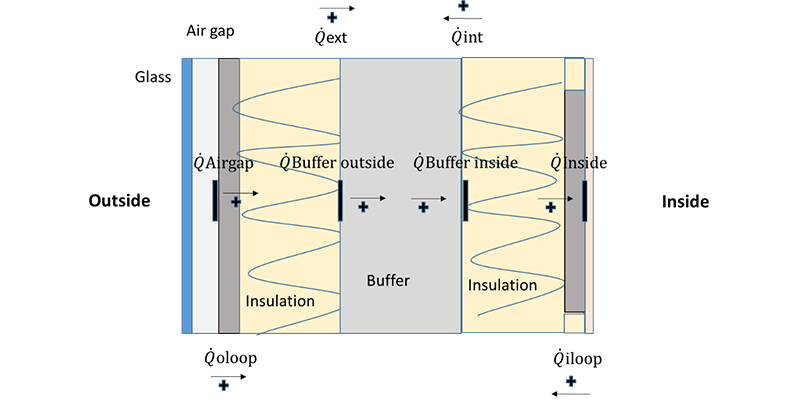
Building envelope systems that integrate Phase Change Materials (PCMs) are solutions aimed at increasing the thermal energy storage potential of the building envelope while keeping its mass reasonably low. Building envelope components with PCMs can be either opaque or transparent and can be based on different types of PCMs and integration methods. In opposition to conventional building components, these elements present thermal and optical properties that are highly non-linear and depend to a great extent on the boundary conditions. Such a characteristic requires the system development...
-
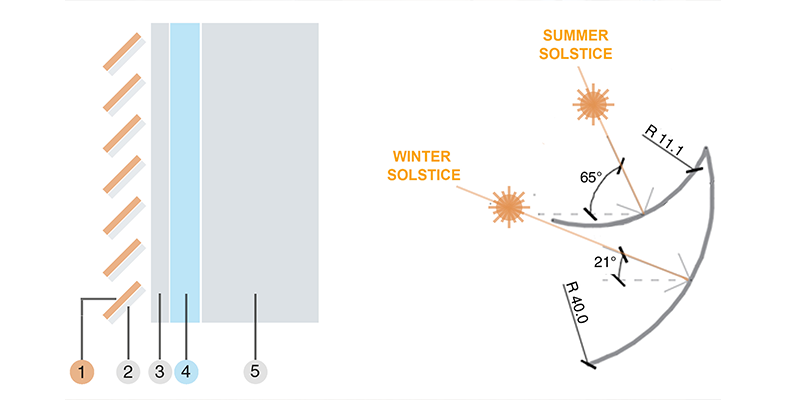
The paper presents the first results of research that was partly conducted within the framework of European COST Action TU1403 – Adaptive Façades Network, on the development of an adaptive BIPV (Building Integrated Photovoltaic) solution able to change its curvature in relation to the external environmental conditions, orientating itself in order to optimise the energy production without the aid of any mechanical and electrical systems. After analysing the characteristics of the main adaptive materials that are currently used for such applications, the contribution outlines the main...
-
163-174
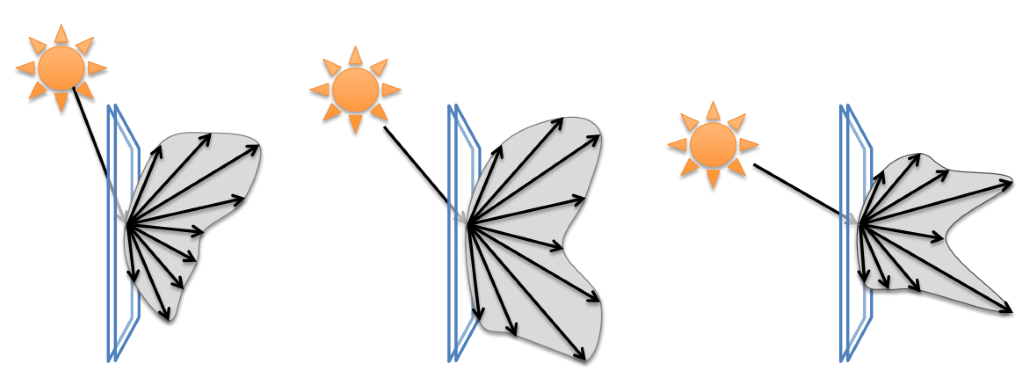
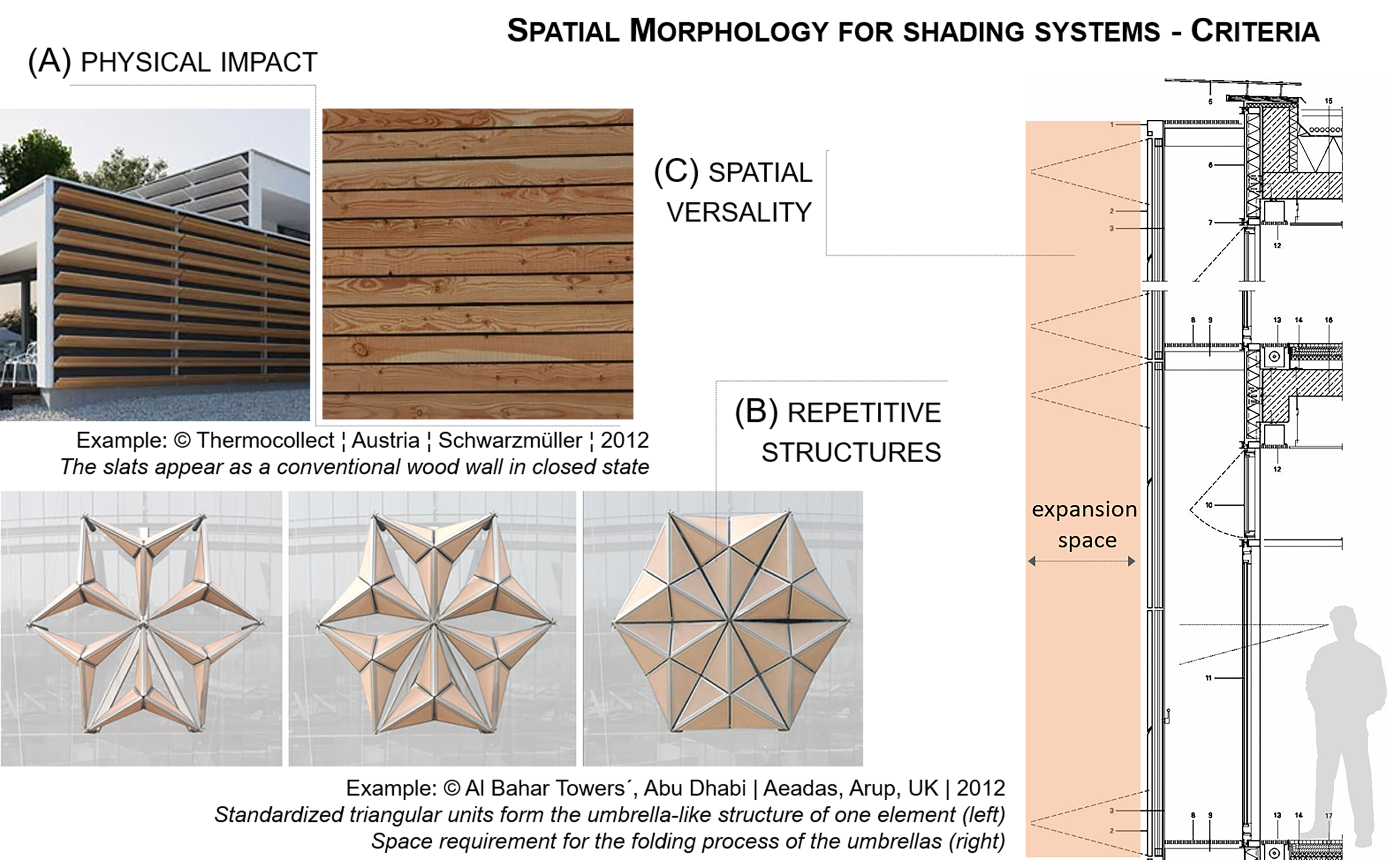
Dynamic shading systems represent the majority of realised adaptive façades. It seems that geometrically complex kinetic solutions have increased in recent years, mainly due to the use of parametric design tools and digital production. In most shading systems, however, geometry rarely plays a guiding role in the design. The kinetic mechanisms are confined to linear or planar geometries. Geometry plays an important role in biological organisms, because it is the decisive factor for efficiency and growth. Their growth patterns could provide new insights for dynamic shading designs. For...
-
175-196
Traditional façade characterisation metrics such as U-value and g-value are of limited value in the design process of buildings with adaptive façades. This issue is particularly important for adaptive façade components that have the capability of controlling thermal energy storage in the construction thermal mass. Building performance simulations can help to analyse the performance of buildings with adaptive façades, but such studies usually only provide information about the energy and comfort performance at room level. Consequently, there is a need for development and testing of new...