Editorial
-
We are proud to announce that we have officially completed the NWO funding period by successfully establishing the Journal. For three years JFDE has been supported by the Open Access Fund of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research NWO (www.nwo.nl). We have been able to publish 40 papers in the first three volumes. That is slightly less than we have hoped but the numbers have steadily increased to 19 papers in volume 3 alone.
We would like to thank NWO for the support. The funding allowed us to cover a large part of the publishing costs. Still, the TUDelft and our...
Articles
-
The basic principle of ‘3D Printing’ is the layer wise production of real parts from virtual data – be it with laser, with power glue, electron beam or UV light processing (Hopkinson, Hague, & Dickens, 2006). The professional application of ‘3D Printing’ is ‘Additive Manufacturing’ (AM) and this opens a fascinating new world of engineering. It offers a selection of reliable building construction materials – done in concrete, aluminium, steel, high performance plastics or glass. (Woodcock, 2011) No matter what applications can be found: to ‘design for function’ rather to ‘design for...
-
237-252
The authors previously proposed integrated-facade-systems comprising different types of external louvers integrated with buckling restraint braces. The systems can be applied to both new and existing buildings, paying attention to the building’s appearance, upgraded structural performance and indoor environment. The authors have studied indoor daylight conditions with louver facades and a research paper was published in this journal (Misawa et al., 2014). This research study reports on the energy conservation performance for louver facades and proposes an External Shading Coefficient...
-
253-272
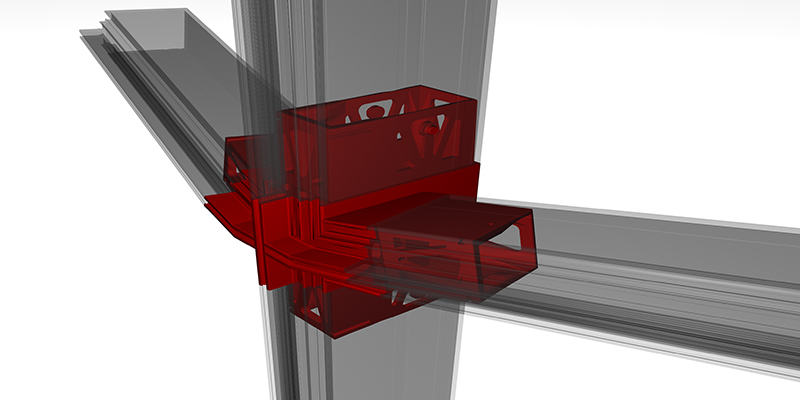
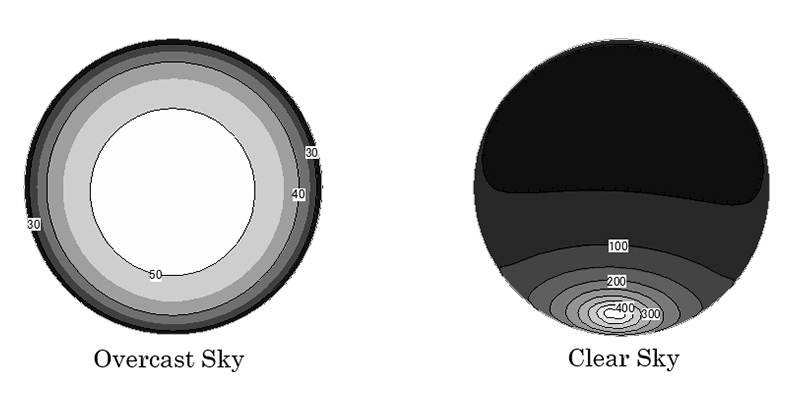
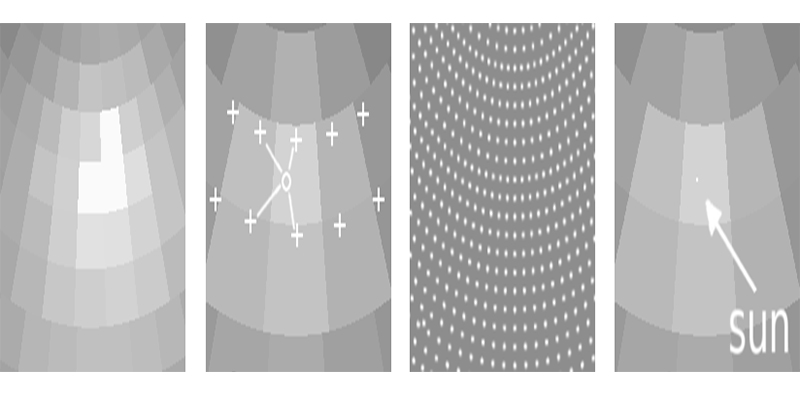
EvalDRC is a newly developed daylight analysis tool for the evaluation of Daylight Redirecting Components (DRC) in architectural spaces. It focuses on the accurate simulation of light redirection with help of the lighting software environment RADIANCE. It employs various key technologies, among them are: a) the daylight coefficient method, b) characterisation of the light redirection behaviour of materials and specially designed systems with appropriate data models, and c) daylight metrics. We present several enhancements to these key technologies and the currently existing tools. In the...
-
273-288
This article deals with the analysis of applied radii in built architecture. This basic evaluation is part of a DFG (largest German research funding organization) research project ‘Basics to develop adaptive formwork systems for free-formed concrete building parts’. It serves to pre-configure adaptive formwork surfaces. The article describes the changes in modern architecture, from rectangular box to free-formed ‘blobs’ in terms of the geometry and the resulting issues of costs and manufacturing process.
-
289-301
Today, an increase of the energy efficiency in the industry is typically achieved by separate, parallel measures, primarily on the level of the individual machines. Energy efficiency can be improved by a holistic, integrated approach, which links the machines, the production process, the technical infrastructure and the building and its envelope.
The subject of this paper is the development of a new prefabricated element for façades and roofs, which was developed and built in the context of a research project called eta-Fabrik (i.e. energy-efficient factory,...