Editorial
-
Welcome to this new issue of our Journal of Façade Design and Engineering. We are very pleased to be able to release a new issue under the current global circumstances, to keep supporting research and the engineering of new technologies, materials, and methods for the design of our envelopes.
This special issue features a wide range of topics, stemming from research activities of members from the European Façade Network (EFN). The EFN seeks to advance and promote façade design and engineering at a European level and beyond, through inclusive collaboration between European Research...
Articles
-
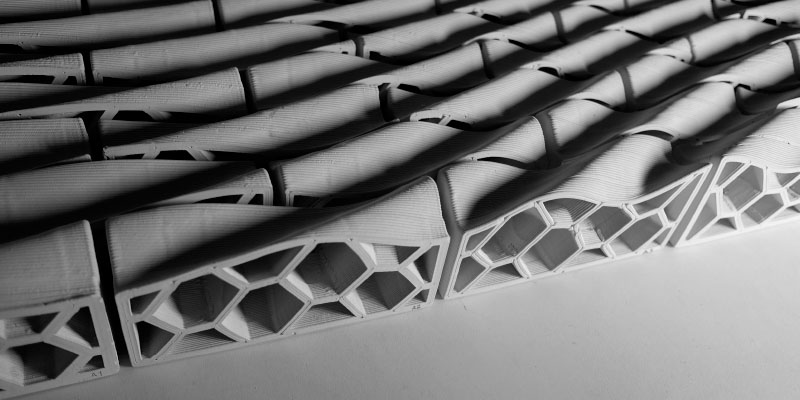
Additive Manufacturing (AM) opens new fields of research and development in the architectural design and construction industry, enabling a geometric freedom that can result in the design of components with specific requirements and multifunctional behaviours.
This work explores the integration of digital design tools and AM extrusion processes on the production of ceramic architectural components for façade construction, reshaping and expanding the boundaries of what is possible to achieve with masonry construction in a wide range of applications (opaque walls, ventilated...
-
43-64
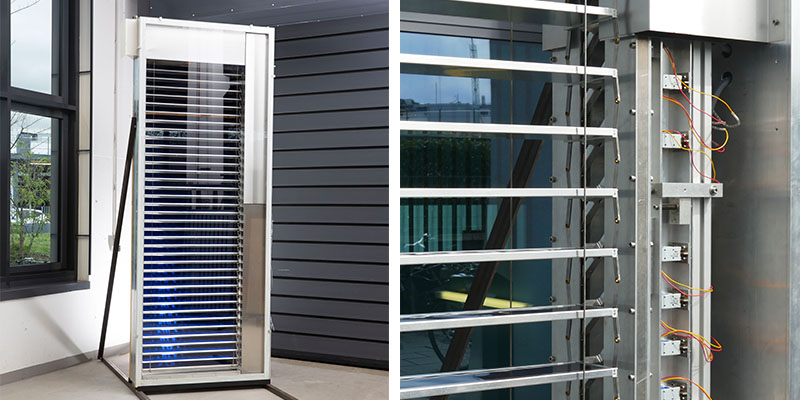
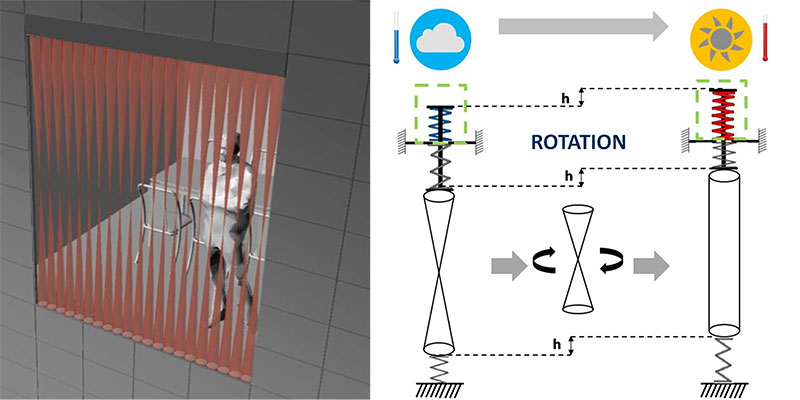
A shading device for façade application was developed by combining twisting cylindrical shading elements with the smart use of shape-memory alloy (SMA) components. These allow a dynamic behaviour of a shading device, which does not require electrical motors or manual activation, nor sophisticated electronic controls. The technical development of the system involved research of cylindrical shading geometries, which can transition from straight to hourglass configuration, given a 180° rotation, with limited mechanical movement. This is induced by the stroke of a SMA spring, which functions...
-
65-84
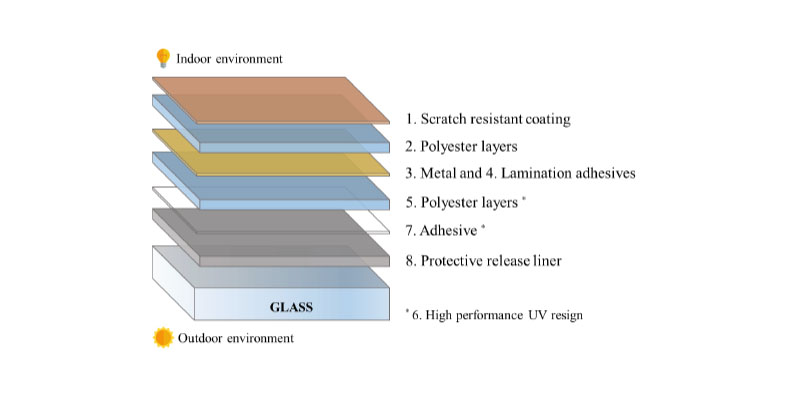
Daylight illuminance levels and their spatial distribution are important design elements to achieve indoor visual comfort conditions and sustainability in buildings during the operation stage. While a proper daylighting scheme increases the efficiency of the building, the excessive use of glazed surfaces can contribute to thermal and visual discomfort, hence increasing the cooling demand and use of artificial lighting. Solar control film (SCF) is a self-adhesive thin film that can be applied on glazing systems of existing buildings for...
-
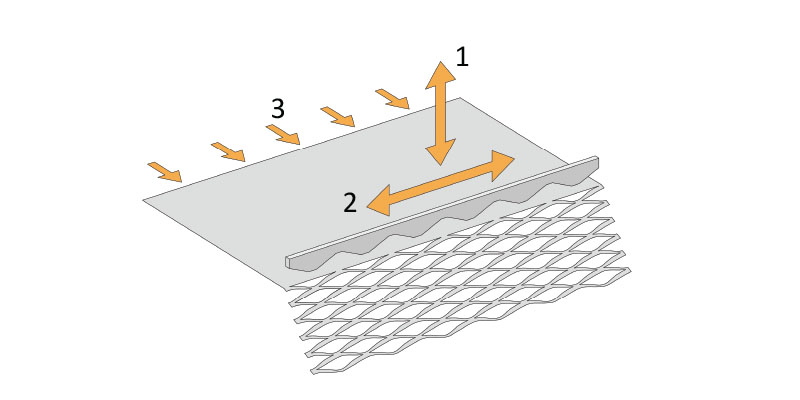
Due to the substantial need for energy efficiency, the daylight performance of building envelopes is a key issue in sustainable architecture. A frequently used shading system consists on static expanded metal meshes (EM). As a very prominent textural facade element, expanded metal is widely used as both a cladding and static shading device.
One first aim is to provide a sufficient description of EM, including fabrication, possible usage and overall properties. This includes a set of parameters needed to control accurately the complex geometry of EM. Those parameters are also...
-
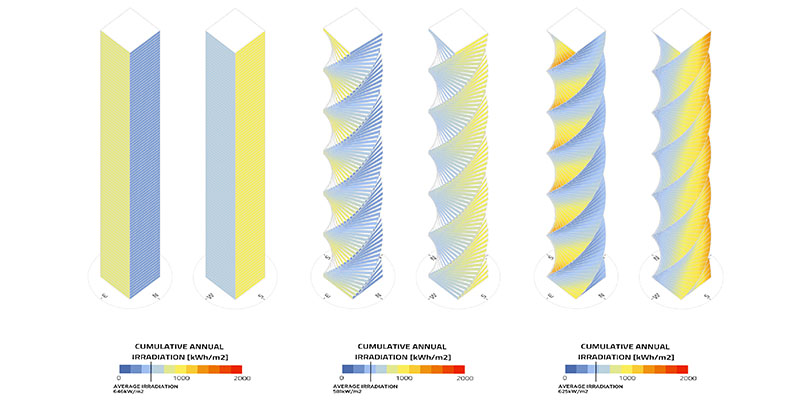
Over the last number of decades, tall building geometries have been shifting from rectangular boxes towards shapes that are defined through geometrical transformations such as twisting. While, from an aesthetical point of view, these twisting geometries make tall buildings appear contemporary and iconic, from an environmental point of view, however, the benefits are not as straightforward. They may vary significantly based on climatic loads and urban conditions, among others.
This study aims to assess the self-shading benefits of twisting geometries by finding a correlation...
-
131-156
Solar thermal venetian blinds (STVB) pursue the goal of reducing the primary energy demand of buildings with highly transparent façades during operation. They can provide solar control and daylighting functions and at the same time function as a solar thermal collector. A technical overview of STVB based on a design parameter space, which can be used as guideline for the design of STVB, is presented. It is then applied to develop a first actual-size test sample of STVB. The design principle, based on heat pipes and a switchable thermal coupling for heat transfer between the slats and a...
Applied practice
-
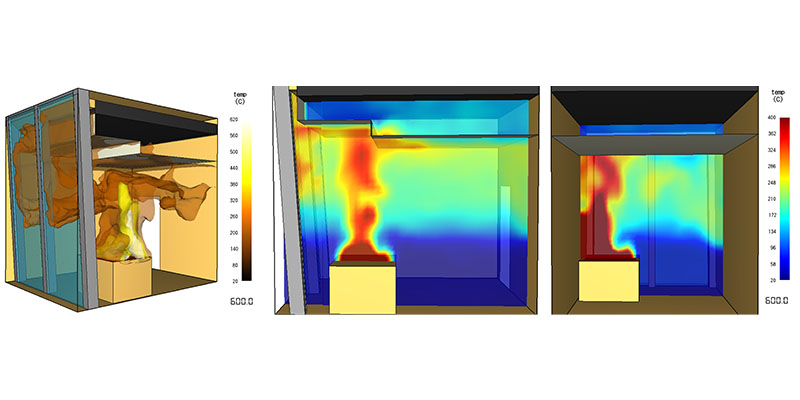
21-42
Nowadays the construction industry is characterised by high multifunctional and complex buildings with innovative façade systems. Unlike a simple prescriptive approach according to standards and codes, a performance-based design allows to define safety levels and goals, to evaluate heat transfer to the structure and the structure response based on fire behaviour, to model different fire scenarios by Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software and to personalize the design according to a specific project in order to reach the required level of safety. Through a significant case study, the...