Editorial
-
We are proud to publish a new issue of the Journal of Façade Design and Engineering. This first issue of volume 10 covers a broad range of themes such as adaptivity, automation, circularity, refurbishment, daylight, acoustics, and user interaction are addressed by peer-reviewed articles.
We would also like to take this opportunity to share some changes in the JFDE editorial team and publishing process. Prof. Tillmann Klein is changing his role from editor-in-chief to editorial board member. Tillmann Klein has been a front-runner in...
Articles
-
In the field of construction practice, decisions regarding material selection frequently come down to a choice based on tradition, i.e. recommendations based on the experience of the engineers hired by an employer as designers, contractors, or energy efficiency engineers. In the presented research, in addition to the Employer, technical individuals were involved in the decision-making process. The harmonisation of Employer opinions and those of experts were obtained through NGT technique and Delphi based method, due to the fact that different criteria for a decision could represent a...
-
29-54
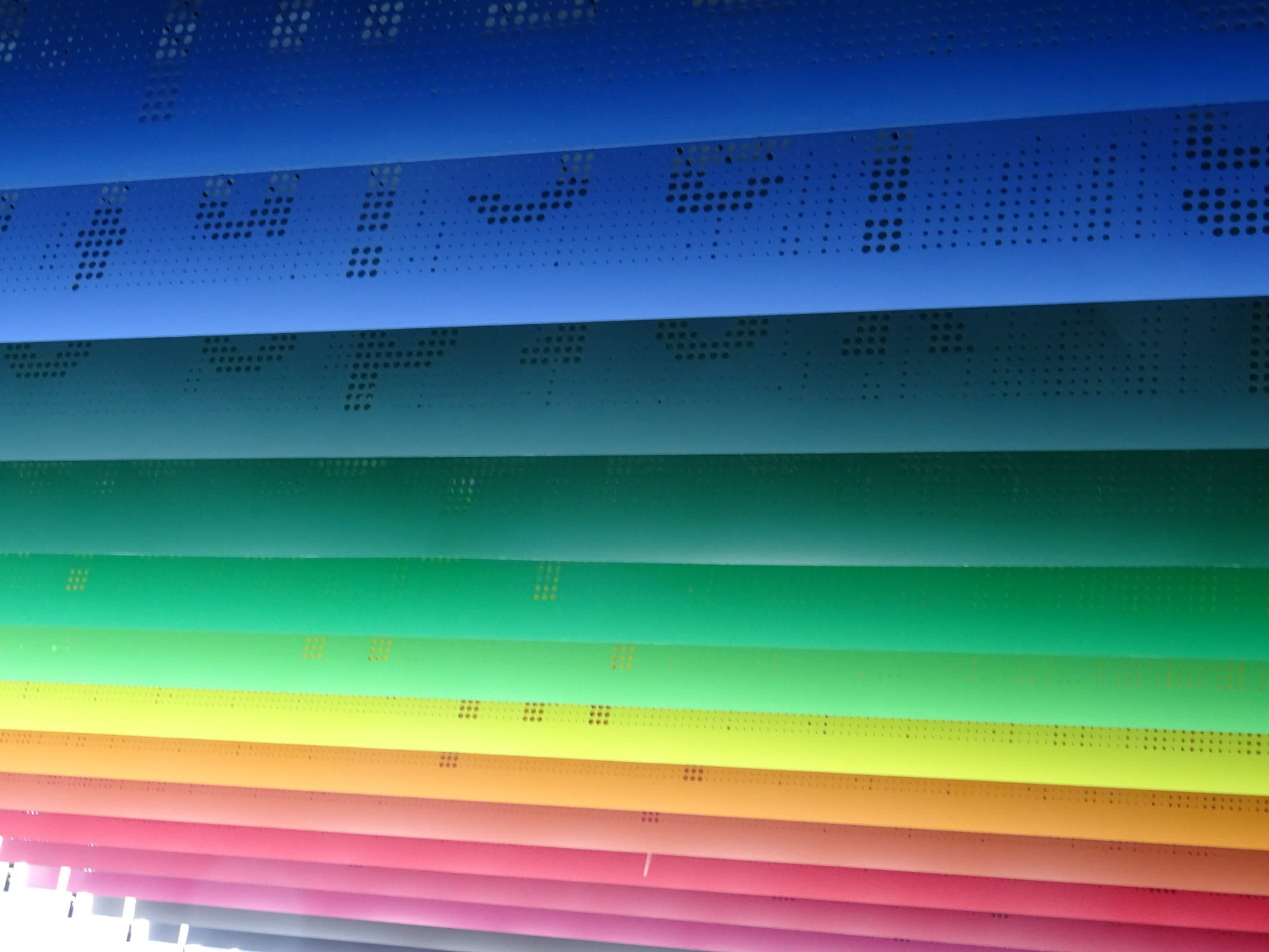
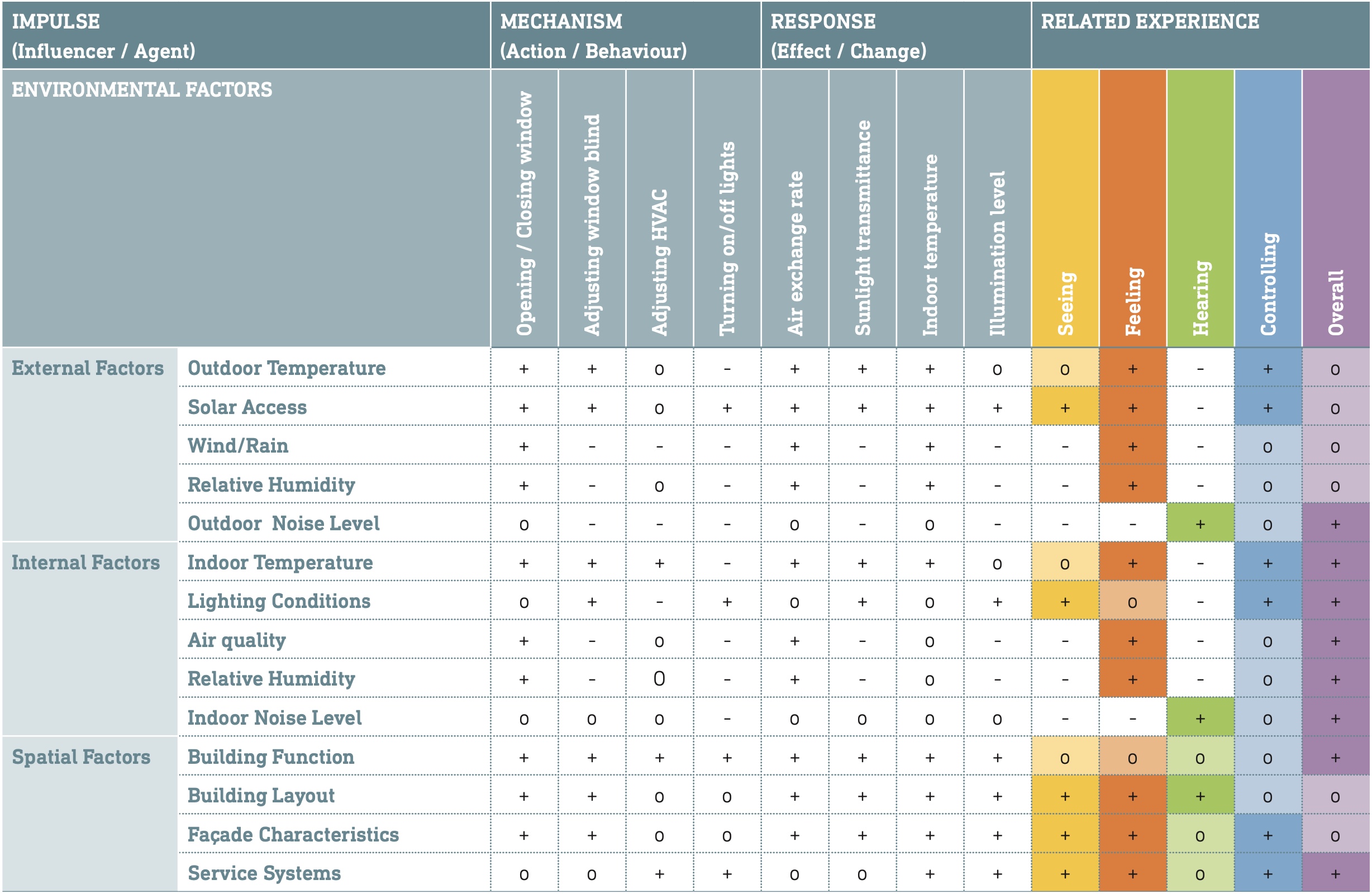
Adaptive façades are multifunctional systems that are able to change their functions, features, or behaviour over time in response to changing boundary conditions or performance requirements. As one of the significant developments in the façade industry over the last decade, the adaptive façade offers an intelligent solution that can decrease energy consumption and potentially increase users’ comfort in a building. From an engineering perspective, these advanced technologies aim to improve the overall performance of the building while generating a better indoor environment for the users,...
-
55-74
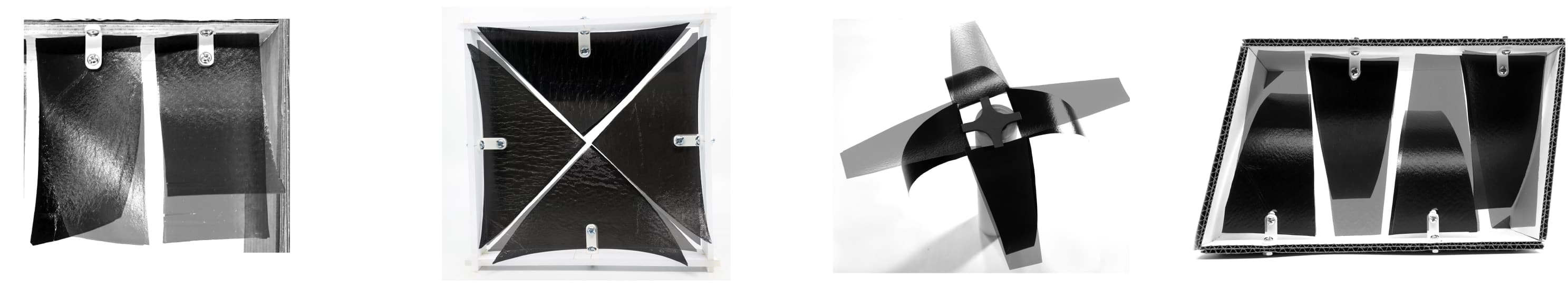
Bistable laminates are composite structures that exhibit more than one static configuration, showing a "snap-through" behaviour that results from residual stresses generated during the curing process. This study focuses on finding adequate fibre and laminate arrangements for bistable laminates used in functional kinetic shadings. We present a study with a mixed-methods approach, combining experimental prototyping and performance simulation studies. We fabricated and analysed the geometry of a series of prototypes, conducting daylight studies to assess the performance of different...
-
75-105
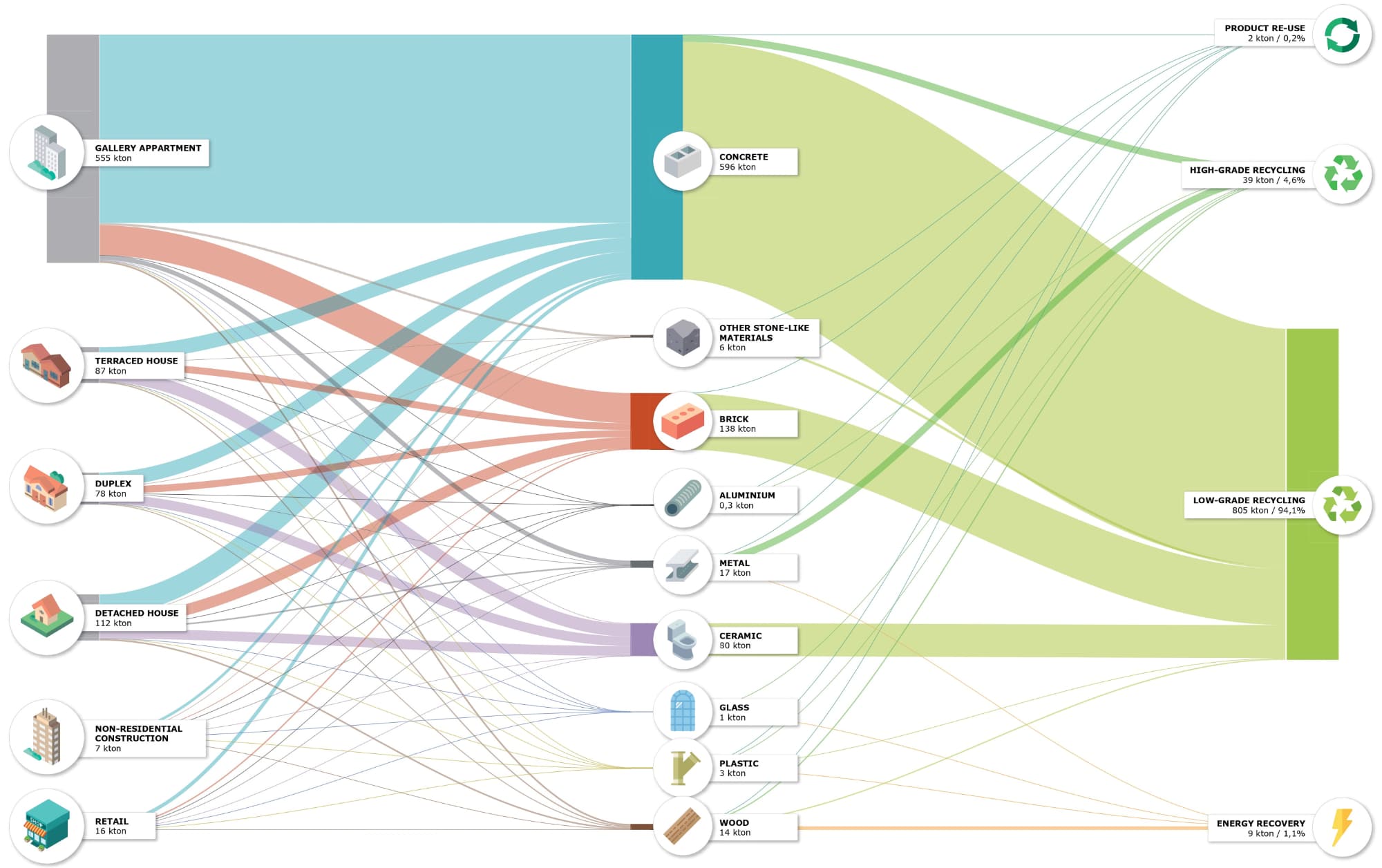
Many studies concerning lowering the Operational Energy (OE) of existing dwellings have been conducted. However, those studies barely cover its collateral Embodied Energy (EE). As the Circular Economy is gaining momentum and the balance between OE and EE is shifting, the Life Cycle Energy Performance (LCEP) is becoming increasingly relevant as an indicator. LCEP accounts for all the OE and EE a building consumes during its lifespan. However, clear insights into the LCEP are still to be investigated. This study focuses on developing a circular and energy-efficient renovation solution for...
-
105-118
This paper evaluates how parts of the building engineering design processes can be automated using software automation, with a focus on the analysis of thermal bridges in façades. Reduced repetition in façade design requires the automation of routine tasks that would otherwise be performed manually. Because full software automation is seldom achievable, a preliminary decision-making process that considers both the effort to create automation and the benefit to exploit it is required. A methodology is presented to achieve beneficial trade-offs between effort and benefits, by using...
-
The thermal performance of adaptive building envelopes can be evaluated using building performance simulation tools. Simulation capabilities and accuracy in predicting the dynamic behaviour of adaptive building envelopes can be enhanced through co-simulation. However, it is unclear how accurately co-simulation can predict the performance of adaptive building envelopes and how the accuracy of adaptive building envelope models created in co-simulation setups can be assessed and validated. Therefore, this study presents new evidence on the empirical validation of co-simulation setups for...
-
External sun shading devices are increasingly used in sustainable buildings to reduce the greenhouse effect in the summer and the glare effect due to direct solar irradiation through transparent surfaces. The acoustic effects of these devices have been investigated in recent studies that suggest the possibility of optimising these elements to improve acoustic comfort in indoor environments, even with open windows. Nevertheless, there are few studies that analyse the combined effect of these devices on acoustic attenuation and improved daylighting....